
Services
Pneumonia
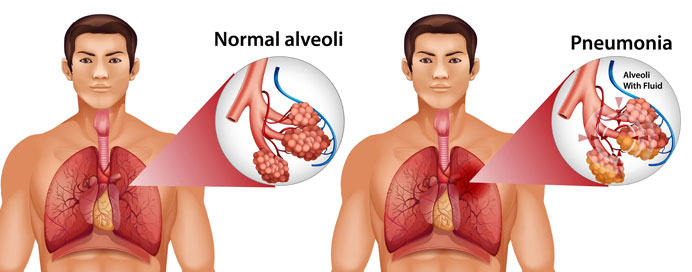
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection characterized by inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs, typically caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms. It can range from mild to severe and is a leading cause of illness and death worldwide, particularly among the very young, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. Symptoms of pneumonia may include cough, fever, chills, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and fatigue. Diagnosis often involves a combination of physical examination, chest X-ray, and laboratory tests such as sputum culture or blood tests. Treatment depends on the cause of the pneumonia but may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral infections, and supportive care such as rest, hydration, and pain relief. Vaccines are available to prevent certain types of pneumonia, including the pneumococcal vaccine and the influenza vaccine, which can significantly reduce the risk of infection, especially in high-risk populations. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial in preventing complications and improving outcomes for individuals affected by pneumonia.
