
Services
Foreign Body Obstruction
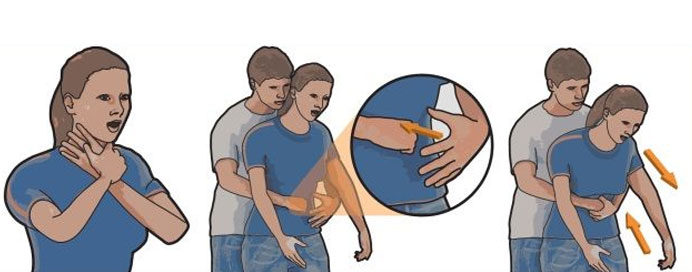
Foreign body obstruction occurs when a foreign object becomes lodged in the airway, blocking airflow into the lungs. This obstruction can lead to potentially life-threatening respiratory distress if not promptly addressed. Common causes include inhaling small objects, such as food particles, toys, or other small items, particularly in children. Symptoms of foreign body obstruction can vary depending on the location and size of the object but may include coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, choking, and in severe cases, cyanosis (blue skin color) due to lack of oxygen. Treatment involves immediate first aid maneuvers such as back blows or abdominal thrusts to dislodge the object, followed by advanced medical intervention if necessary, including bronchoscopy to remove the object under direct visualization. Prompt recognition and appropriate management are essential to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcome for individuals experiencing foreign body obstruction.
