
Services
Intercostal Drainage Tube
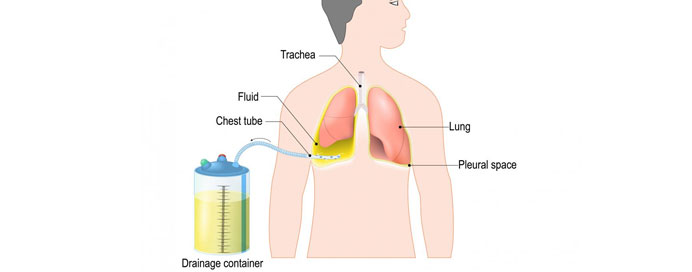
An intercostal drainage tube, also known as a chest tube or chest drain, is a medical device used to remove air, blood, or other fluids from the pleural space—the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure, known as chest tube insertion or intercostal drainage, is commonly performed to treat conditions such as pneumothorax (collapsed lung), pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid), or hemothorax (blood in the pleural space) that can impair lung function and lead to respiratory distress. During the procedure, a flexible tube is inserted through a small incision in the chest wall and positioned within the pleural space, allowing trapped air or fluid to drain out, thus re-expanding the lung and relieving pressure on the chest. The tube is connected to a drainage system that collects and measures the fluid being removed. Chest tube placement is typically performed under local anesthesia or sedation and may require monitoring in a hospital setting until the underlying condition is adequately treated. While chest tube insertion carries certain risks, including infection or injury to surrounding structures, it is an essential intervention in managing various thoracic emergencies and restoring normal respiratory function.
